Library
Answer to the Question of the week -1
- February 19, 2020
- Posted by: Namrata Chhabra
- Category: Image Challenge Metabolism of Carbohydrates Multiple-choice questions Multiple-choice questions Practice questions
A 23-year-old bodybuilder visits his physician with complaints of fatigue, depression, insomnia, hair loss, and dry skin. He tells the physician he has been “bulking up” for an upcoming competition, and his meals consist mostly of eight raw eggs along with low-fat milk. The physician suspects biotin deficiency, given the patient’s diet and symptoms. Which of the following is biotin required for?
- The formation of cis-retinal
- Transfer of 1-carbon units
- Hydroxylation reactions
- Carboxylation of pyruvate
- Decarboxylation of α-Keto acids
Answer- D- Carboxylation of pyruvate is the right answer. Biotin is required for carboxylation reactions. The common examples are-
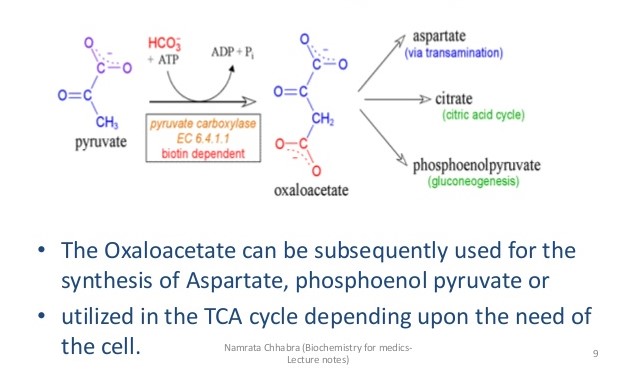
a) Conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate- The first step of gluconeogenesis. The reaction is catalyzed by pyruvate carboxylase (figure).
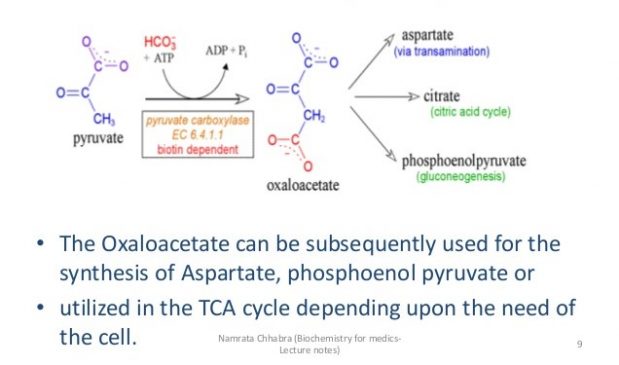
Figure- Pyruvate to Oxaloacetate conversion
b) Conversion of Acetyl CoA to Malonyl CoA- The first step of fatty acid synthesis. The reaction is catalyzed by Acetyl CoA carboxylase.
c) Conversion of Propionyl CoA to D-methyl malonyl CoA. The reaction is catalyzed by propionyl CoA carboxylase. Propionyl CoA is utilized in the TCA cycle through the formation of succinyl CoA. D and L- methyl malonyl CoA are formed during the process of conversion of propionyl co A to succinyl co A.
In the given situation, signs and symptoms of the patient are highly suggestive of egg white injury that occurs upon consumption of raw eggs. Biotin present in egg yolk binds with Avidin of egg white due to its great affinity for Avidin, making a nonfunctional Biotin- Avidin complex. A deficiency of biotin is precipitated that is manifested by hair loss; premature graying of hair, brittle nails, and dry skin. Biotin is considered a “beauty vitamin” due to its role in the maintenance of skin, hair, and nails.
As regards other options-
- The formation of cis-retinal is mediated by Vitamin A.
- Transfer of 1-carbon units is carried out by folic acid
- Hydroxylation reactions require vitamin C as a coenzyme
- Decarboxylation of α-Keto acids is carried out by Thiamine. Multienzyme complexes are involved that also require pantothenic acid, lipoic acid, riboflavin, and niacin. The examples are PDH complex, α- Keto glutarate dehydrogenase complex, α- Keto acid dehydrogenase complex, etc.
Author:Namrata Chhabra
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
