Library
Elevated Acyl carnitine compounds and associated hypoglycemia- What is the defect?
- February 28, 2020
- Posted by: Namrata Chhabra
- Category: Energy metabolism Learning resources Library Metabolism of lipids Multiple-Choice questions Multiple-choice questions Practice questions USMLE Content USMLE Style questions USMLE styled question bank
Case details
A 5- year-old boy suffered gastroenteritis for two days and was brought to the emergency in a semiconscious state. Blood glucose at the time of admission was 45 mg/dl and his urine was negative for glucose and ketone bodies. Glucose was administered intravenously, and his condition improved within 10 minutes. Subsequent laboratory investigations revealed elevated acylcarnitine residues. The child was diagnosed with an enzyme deficiency. The parents were instructed to feed the child more frequently.
Which of the following enzymes might be deficient?
- Acyl CoA synthetase
- Carnitine Acyl transferase-1
- Translocase
- Carnitine Acyl transferase-2
- Acyl CoA dehydrogenase
The correct answer is- A. Acyl CoA dehydrogenase.
Acyl CoA synthetase catalyzes the activation of fatty acid to form Fatty acyl CoA, the active form of fatty acid (figure-1).
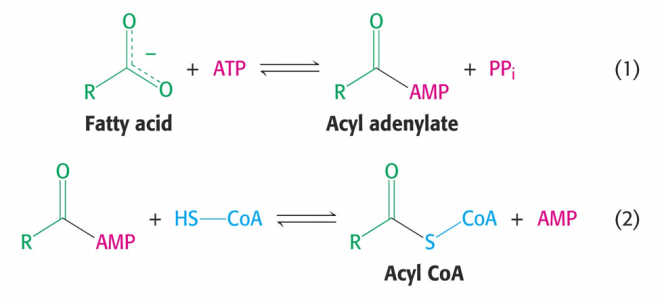
Figure-1- reaction catalyzed by Acyl co A synthetase
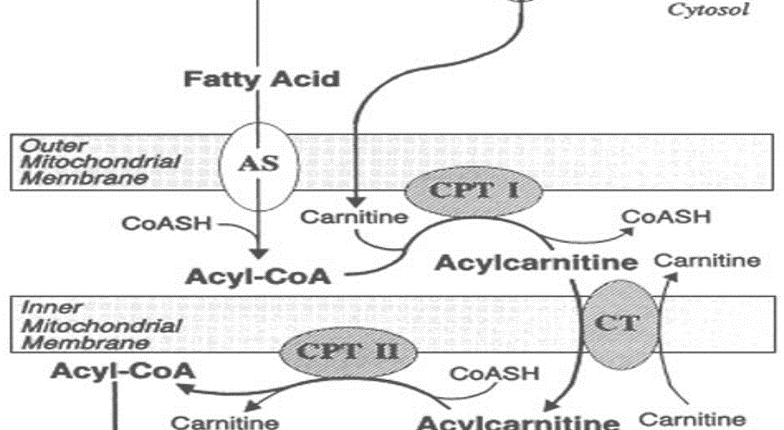
Carnitine Acyl transferase-1(CAT-1), Translocase, and Carnitine Acyl transferase-2(CAT-2) are the components of the carnitine shuttle (Figure 2), which is required for the transportation of fatty acyl CoA across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
a) CAT-1 catalyzes the conversion of Acyl CoA to Acyl carnitine.
b) Translocase transports acylcarnitine across the inner mitochondrial membrane in exchange for carnitine.
c) CAT-2 catalyzes the conversion of Acyl carnitine back to Acyl CoA, the form that is required for the beta-oxidation of acyl CoA by the enzymes present in the mitochondrial matrix.
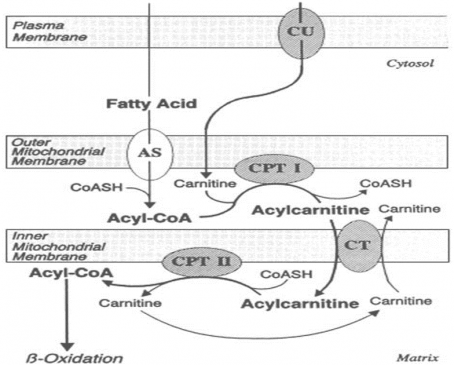
Figure 2- Role of carnitine in the transport of long-chain fatty acids through the inner mitochondrial membrane. Long-chain acyl-CoA cannot pass through the inner mitochondrial membrane, but its metabolic product, acylcarnitine, can cross through with the help of a carnitine shuttle. CPT (Carnitine palmitoyl transferase), is specific for Palmitic acid, which is the most abundant fatty acid, AND Acyl is a general term for fatty acid.
Mitochondrial beta-oxidation is a cyclic process. In each cycle, the fatty acyl CoA is subjected to four chemical processes. Two carbons are removed as Acetyl CoA from the parent compound in each cycle. The chemical processes involved in each cycle are :
1) Dehydrogenation
2) Hydration
3) Dehydrogenation, and
4) Thiolytic cleavage.
These cycles are repeated till the fatty acid is completely broken down into the final two carbon compounds.
Acyl CoA dehydrogenase is the first enzyme in the cyclic process of beta-oxidation. It catalyzes the conversion of acyl CoA to α,β Unsaturated Acyl CoA.
The deficiency of Acyl CoA dehydrogenase impairs beta-oxidation.
Hypoglycemia in this condition is a consequence of impaired fatty acid oxidation with the resultant imbalance between the demand and supply of glucose, which is the sole source of energy in such individuals.
Author:Namrata Chhabra
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
