Library
Summary- Regulation of Major Pathways Of Carbohydrate metabolism
- February 24, 2020
- Posted by: Namrata Chhabra
- Category: Quick Revision Series Energy metabolism Learning resources Library Metabolism of Carbohydrates Quick revisions Quick revisions
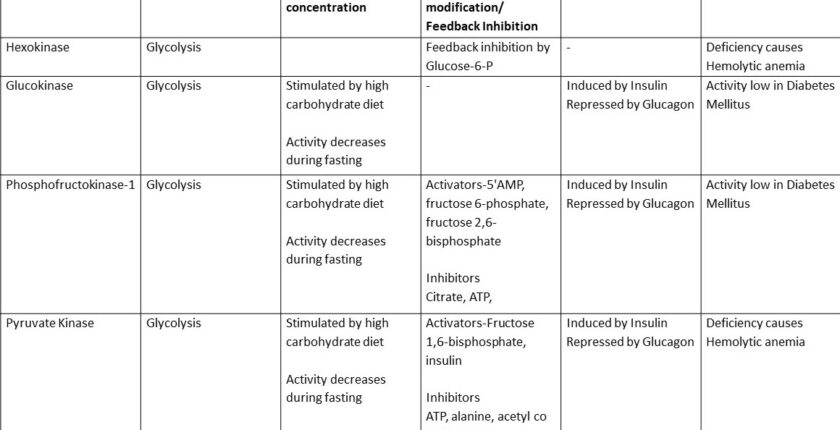
| Enzyme | Pathway | Effect of Substrate Concentration | Allosteric Modification/ Feedback Inhibition | Induction/Repression | Clinical Significance |
| Hexokinase | Glycolysis | Feedback inhibition by Glucose-6-P | – | Deficiency causes Hemolytic anemia. | |
| Glucokinase | Glycolysis | Stimulated by a high carbohydrate diet
Activity decreases during fasting |
– | Induced by Insulin
Repressed by Glucagon |
Activity low in Diabetes Mellitus |
| Phosphofructokinase-1 | Glycolysis | Stimulated by a high carbohydrate diet
Activity decreases during fasting |
Activators-5’AMP, fructose 6-phosphate, fructose 2,6-bisphosphate InhibitorsCitrate, ATP, |
Induced by Insulin
Repressed by Glucagon |
Activity low in Diabetes Mellitus |
| Pyruvate Kinase | Glycolysis | Stimulated by a high carbohydrate diet
Activity decreases during fasting |
Activators-Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, insulin
Inhibitors ATP, alanine, acetyl co A glucagon |
Induced by Insulin
Repressed by Glucagon |
Deficiency causes Hemolytic anemia |
| Pyruvate dehydrogenase | Pyruvate to Acetyl Co A | Stimulated by a high carbohydrate diet
Activity decreases during fasting |
Activators-CoA, NAD+, insulin, ADP, pyruvate
Inhibitors Acetyl CoA, NADH, ATP (fatty acids, ketone bodies) |
Deficiency causes Lactic acidosis | |
| Pyruvate carboxylase | Gluconeogenesis | Inhibited by a high carbohydrate diet
Stimulated during fasting |
Activator-Acetyl CoA
Inhibitor ADP |
Induced by Glucocorticoids, glucagon, epinephrine
Repressed by Insulin |
Activity increases in Diabetes Mellitus |
| Fructose 1,6 bisphosphatase | Gluconeogenesis | Inhibited by a high carbohydrate diet
Stimulated during fasting |
Activator-Citrate
Inhibitor AMP, Fr 2,6 bisphosphate |
Induced by Glucocorticoids, glucagon, epinephrine
Repressed by Insulin |
Activity increases in Diabetes Mellitus |
| Glucose-6-P dehydrogenase | HMP pathway | Stimulated by a high carbohydrate diet
Activity decreased during fasting. |
Activator-NADP+ | Induced by Insulin | Deficiency Causes Hemolytic anemia |
| Glycogen
Synthase |
Glycogenesis | Stimulated by a high carbohydrate diet
Activity decreased during fasting |
Activator-Glucose and Glucose-6-P
and Insulin (By causing dephosphorylation) Inhibitor- Glucagon (By cAMP-mediated phosphorylation)
|
Deficiency causes Type-0 Glycogen
Storage disease |
|
| Glycogen Phosphorylase | Glycogenolysis | Stimulated during fasting
Inhibited in the fed state |
Activator-Ca ++, Low Glucose concentration, Glucagon (By c AMP mediated phosphorylation)
Inhibitor-Insulin (By causing dephosphorylation)
|
Muscle phosphorylase deficiency causes V Glycogen storage disease (McArdle’s syndrome)
Liver phosphorylase deficiency causes Type VI Glycogen storage disease (Her’s disease) |
Author:Namrata Chhabra
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
