Quick Revision Series
Our Biochemistry > Quick Revision Series
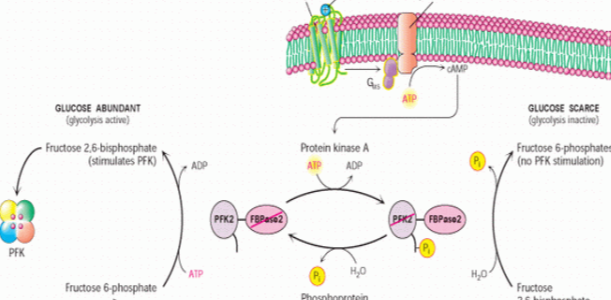
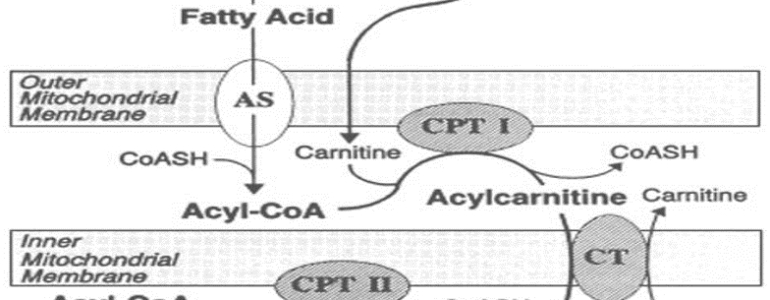
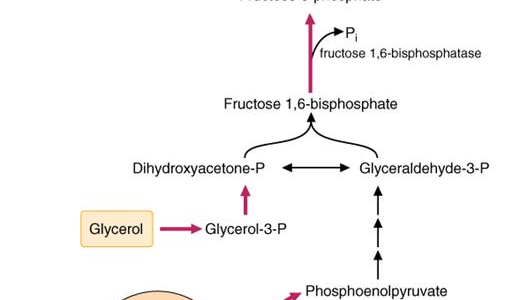
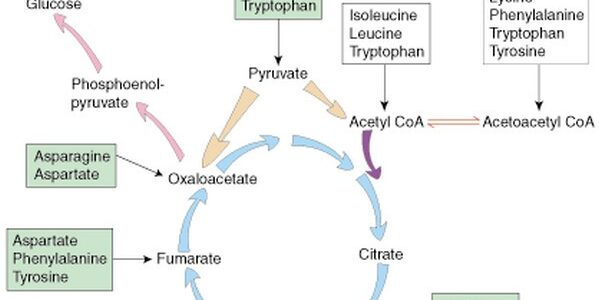
Comprehensive Overview of Fatty Acid Metabolism Disorders: Key Enzyme Defects, Clinical Manifestations, and Mnemonics for Easy Recall
09
Nov
Posted in:
Energy metabolism ,
Learning resources ,
Library ,
Metabolism of lipids ,
Quick Revision Series ,
Quick revisions ,
Quick revisions ,
USMLE Content ,
Glycogen Storage Diseases- Multiple-Choice Questions
04
Nov
Posted in:
Energy metabolism ,
Learning resources ,
Library ,
Metabolism of Carbohydrates ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Multiple-Choice questions ,
Practice questions ,
Practice questions ,
Question Bank ,
Question Bank ,
Quick Revision Series ,
USMLE Content ,
USMLE Style questions ,
USMLE styled question bank ,