Learning resources
Our Biochemistry > Learning resources
“Master Transcription with Case-Based MCQs: Test Your Understanding!”
04
Apr
Posted in:
Learning resources ,
Library ,
Molecular Biology ,
Molecular Biology ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Multiple-Choice questions ,
Practice questions ,
Question Bank ,
Question Bank ,
USMLE Content ,
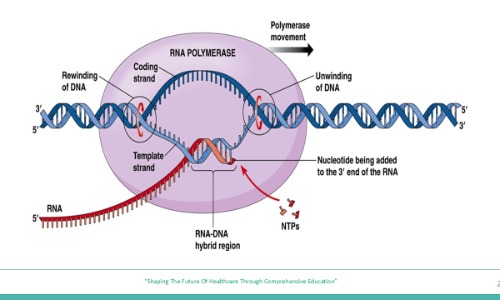
Understanding DNA Transcription and Post-Transcriptional Modifications: Key Mechanisms and Clinical Implications
20
Mar

Explore the intricate process of DNA transcription and post-transcriptional modifications, including mRNA processing, splicing, and regulatory mechanisms. Learn about their significance in gene expression, protein synthesis, and disease pathogenesis.
Posted in:
Learning resources ,
Library ,
Molecular Biology ,
Molecular Biology ,
PowerPoint Presentations ,
PowerPoint presentations ,
DNA Damage Repair: Mechanisms, Clinical Implications, and Therapeutic Advances
19
Mar

Posted in:
Learning resources ,
Library ,
Molecular Biology ,
Molecular Biology ,
PowerPoint Presentations ,
PowerPoint Presentations ,
PowerPoint presentations ,
USMLE Content ,
Tags:
Biomedical Science,
Cancer research,
Cancer Therapy,
Cell Cycle Regulation,
DNA Damage Repair,
DNA Repair Inhibitors,
DNA Repair Mechanisms,
DNA Repair Pathways,
Genetic Mutations,
Genetic Stability.,
Genomic Stability,
Homologous Recombination,
mismatch repair,
Molecular Medicine,
Mutations and Disease,
oncogenes,
Precision Medicine,
Targeted Cancer Treatments,
Translational Medicine,
tumor suppressor genes,
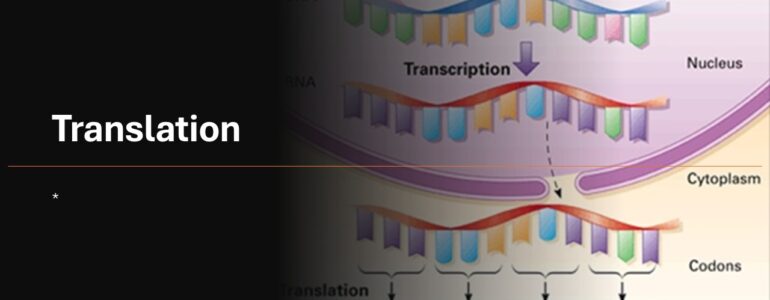
Genetic Code and Translation: Deciphering the Blueprint of Life
17
Mar
Posted in:
Learning resources ,
Library ,
Molecular Biology ,
Molecular Biology ,
Multiple-Choice questions ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Practice questions ,
Question Bank ,
Question Bank ,
USMLE Content ,
USMLE Style questions ,
USMLE styled question bank ,
Understanding DNA Repair: 15 High-Yield Case-Based Questions
16
Mar

Test your knowledge of DNA damage and repair with 15 case-based multiple-choice questions (MCQs). This post covers essential repair mechanisms, including homologous recombination, base excision repair, mismatch repair, and nucleotide excision repair, with clinical applications in genomic instability, cancer biology, and radiation sensitivity. A must-read for medical students, geneticists, and oncology researchers!
Posted in:
Learning resources ,
Library ,
Molecular Biology ,
Molecular Biology ,
Multiple-Choice questions ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Practice questions ,
Question Bank ,
Question Bank ,
USMLE Content ,
USMLE Style questions ,
USMLE styled question bank ,
25 Case-Based MCQs on Cytoskeleton: Test Your Medical Knowledge!
06
Mar

Ever wondered how the cytoskeleton supports cellular structure and movement? 🧬 Dive into 25 case-based multiple-choice questions that challenge your understanding of microtubules, actin filaments, intermediate filaments, and cytoskeletal disorders. Ideal for medical students, USMLE prep, and cell biology learners. Let’s test your knowledge!
Posted in:
Cell Biology ,
Cell Biology ,
Learning resources ,
Library ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Multiple-Choice questions ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Practice questions ,
Question Bank ,
Question Bank ,
USMLE Content ,
USMLE Style questions ,
USMLE styled question bank ,
Case-Based MCQs on RNA Structure and Function: Test Your Knowledge
05
Mar
Posted in:
Learning resources ,
Library ,
Molecular Biology ,
Molecular Biology ,
Multiple-Choice questions ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Practice questions ,
Question Bank ,
Question Bank ,
Quizzes ,
USMLE Content ,
USMLE Style questions ,
USMLE styled question bank ,
DNA & RNA: Structure, Functions, and Biological Significance | Molecular Biology PPT
05
Mar

Deep dive into the structure and functions of DNA & RNA. This PPT covers their molecular composition, roles in biology, and key differences in detail
Posted in:
Learning resources ,
Library ,
Molecular Biology ,
Molecular Biology ,
PowerPoint Presentations ,
PowerPoint presentations ,
USMLE Content ,
Tags:
base pairing rules,
biological macromolecules,
biological structure,
cellular molecules,
DNA double-helix,
DNA functions,
DNA structure,
DNA vs. RNA comparison,
genetic material.,
life sciences,
molecular biology fundamentals,
nucleic acids,
nucleotides and base pairs,
RNA functions,
RNA single-stranded,
RNA structure,
Case-Based Multiple-Choice Questions on DNA Structure and Organization
04
Mar

Understanding DNA structure and organization is crucial in molecular biology and medicine. This guide covers key concepts like nucleosome assembly, euchromatin vs. heterochromatin, histone modifications, and DNA packaging, with exam-style case-based questions to enhance learning.
Posted in:
Learning resources ,
Library ,
Molecular Biology ,
Molecular Biology ,
Multiple-Choice questions ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Practice questions ,
Question Bank ,
Question Bank ,
Quizzes ,
USMLE Content ,
USMLE Style questions ,
USMLE styled question bank ,
50 Essential Questions on the Structure & Functions of DNA & RNA – Strengthen Your Molecular Biology Foundations
04
Mar

Prepare for higher-order case-based questions by mastering the basics! This post covers 50 key questions on the structure and functions of DNA & RNA, DNA packaging, and chromosome structure
Posted in:
Learning resources ,
Library ,
Molecular Biology ,
Molecular Biology ,
Question Bank ,
Question Bank ,
Quizzes ,
Short-answer questions ,
Short-Answer questions ,
USMLE Content ,
