USMLE styled question bank
Our Biochemistry > USMLE styled question bank
Genetic Mutation Question Bank: Case-Based MCQs with Explanations
12
Apr
Posted in:
Library ,
Molecular Biology ,
Molecular Biology ,
Multiple-Choice questions ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Question Bank ,
Question Bank ,
USMLE Style questions ,
USMLE styled question bank ,
Genetic Code and Translation: Deciphering the Blueprint of Life
17
Mar
Posted in:
Learning resources ,
Library ,
Molecular Biology ,
Molecular Biology ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Multiple-Choice questions ,
Practice questions ,
Question Bank ,
Question Bank ,
USMLE Content ,
USMLE Style questions ,
USMLE styled question bank ,
Understanding DNA Repair: 15 High-Yield Case-Based Questions
16
Mar

Test your knowledge of DNA damage and repair with 15 case-based multiple-choice questions (MCQs). This post covers essential repair mechanisms, including homologous recombination, base excision repair, mismatch repair, and nucleotide excision repair, with clinical applications in genomic instability, cancer biology, and radiation sensitivity. A must-read for medical students, geneticists, and oncology researchers!
Posted in:
Learning resources ,
Library ,
Molecular Biology ,
Molecular Biology ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Multiple-Choice questions ,
Practice questions ,
Question Bank ,
Question Bank ,
USMLE Content ,
USMLE Style questions ,
USMLE styled question bank ,
25 Case-Based MCQs on Cytoskeleton: Test Your Medical Knowledge!
06
Mar

Ever wondered how the cytoskeleton supports cellular structure and movement? 🧬 Dive into 25 case-based multiple-choice questions that challenge your understanding of microtubules, actin filaments, intermediate filaments, and cytoskeletal disorders. Ideal for medical students, USMLE prep, and cell biology learners. Let’s test your knowledge!
Posted in:
Cell Biology ,
Cell Biology ,
Learning resources ,
Library ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Multiple-Choice questions ,
Practice questions ,
Question Bank ,
Question Bank ,
USMLE Content ,
USMLE Style questions ,
USMLE styled question bank ,
Case-Based MCQs on RNA Structure and Function: Test Your Knowledge
05
Mar
Posted in:
Learning resources ,
Library ,
Molecular Biology ,
Molecular Biology ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Multiple-Choice questions ,
Practice questions ,
Question Bank ,
Question Bank ,
Quizzes ,
USMLE Content ,
USMLE Style questions ,
USMLE styled question bank ,
Case-Based Multiple-Choice Questions on DNA Structure and Organization
04
Mar

Understanding DNA structure and organization is crucial in molecular biology and medicine. This guide covers key concepts like nucleosome assembly, euchromatin vs. heterochromatin, histone modifications, and DNA packaging, with exam-style case-based questions to enhance learning.
Posted in:
Learning resources ,
Library ,
Molecular Biology ,
Molecular Biology ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Multiple-Choice questions ,
Practice questions ,
Question Bank ,
Question Bank ,
Quizzes ,
USMLE Content ,
USMLE Style questions ,
USMLE styled question bank ,
20 High-Yield Case-Based MCQs on Trace Elements: Clinical Scenarios & Explanations
23
Feb

Explore 20 high-yield multiple-choice questions on trace elements, covering essential minerals like calcium, iron, zinc, selenium, and copper. Each case-based question is designed to enhance understanding of clinical presentations, metabolic disorders, and diagnostic approaches. Perfect for medical students, healthcare professionals, and exam preparation!
Posted in:
Learning resources ,
Library ,
Minerals ,
Multiple-Choice questions ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Practice questions ,
Question Bank ,
Question Bank ,
Question Bank ,
Quizzes ,
USMLE Content ,
USMLE Style questions ,
USMLE styled question bank ,
Vitamins ,
Tags:
#BiochemistryMCQs,
#ClinicalCase,
Acrodermatitis Enteropthica,
alcohol dehydrogenase,
BIOCHEMISTRY FOR MEDICS,
Carbonic anhydrase,
Clinical biochemistry,
Fluoride,
Flurosis,
High-Yeild MCQs,
Iron,
Iron deficiency anemia,
MedicalQuiz,
Nutrition,
Nutritional Biochemistry,
Selenium,
selenosis,
Trace elements,
Zinc,
USMLE-Style MCQs on Fat-Soluble Vitamins | High-Yield Practice Questions
21
Feb

Get high-yield USMLE-style MCQs on fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) with detailed explanations! Test your knowledge on vitamin deficiencies, toxicities, and clinical applications with realistic board exam questions. Perfect for USMLE Step 1 & Step 2 CK preparation.
Posted in:
Learning resources ,
Library ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Multiple-Choice questions ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Practice questions ,
Question Bank ,
Question Bank ,
Quizzes ,
QUIZZES ,
USMLE Content ,
USMLE Style questions ,
USMLE styled question bank ,
Vitamins ,
Vitamins and Minerals ,
Water-Soluble Vitamins: Clinical MCQs with Explanations & Illustrations
19
Feb
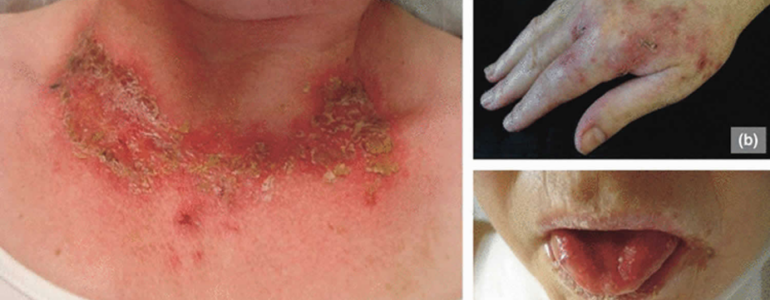
Test your knowledge of biochemistry and clinical medicine with these high-yield, NBME-style multiple-choice questions on water-soluble vitamins. Each question is case-based to enhance clinical reasoning and exam preparedness.
