Practice questions
Our Biochemistry > Practice questions
Case-Based MCQs on RNA Structure and Function: Test Your Knowledge
05
Mar
Posted in:
Learning resources ,
Library ,
Molecular Biology ,
Molecular Biology ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Multiple-Choice questions ,
Practice questions ,
Question Bank ,
Question Bank ,
Quizzes ,
USMLE Content ,
USMLE Style questions ,
USMLE styled question bank ,
Case-Based Multiple-Choice Questions on DNA Structure and Organization
04
Mar

Understanding DNA structure and organization is crucial in molecular biology and medicine. This guide covers key concepts like nucleosome assembly, euchromatin vs. heterochromatin, histone modifications, and DNA packaging, with exam-style case-based questions to enhance learning.
Posted in:
Learning resources ,
Library ,
Molecular Biology ,
Molecular Biology ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Multiple-Choice questions ,
Practice questions ,
Question Bank ,
Question Bank ,
Quizzes ,
USMLE Content ,
USMLE Style questions ,
USMLE styled question bank ,
20 High-Yield Case-Based MCQs on Trace Elements: Clinical Scenarios & Explanations
23
Feb

Explore 20 high-yield multiple-choice questions on trace elements, covering essential minerals like calcium, iron, zinc, selenium, and copper. Each case-based question is designed to enhance understanding of clinical presentations, metabolic disorders, and diagnostic approaches. Perfect for medical students, healthcare professionals, and exam preparation!
Posted in:
Learning resources ,
Library ,
Minerals ,
Multiple-Choice questions ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Practice questions ,
Question Bank ,
Question Bank ,
Question Bank ,
Quizzes ,
USMLE Content ,
USMLE Style questions ,
USMLE styled question bank ,
Vitamins ,
Tags:
#BiochemistryMCQs,
#ClinicalCase,
Acrodermatitis Enteropthica,
alcohol dehydrogenase,
BIOCHEMISTRY FOR MEDICS,
Carbonic anhydrase,
Clinical biochemistry,
Fluoride,
Flurosis,
High-Yeild MCQs,
Iron,
Iron deficiency anemia,
MedicalQuiz,
Nutrition,
Nutritional Biochemistry,
Selenium,
selenosis,
Trace elements,
Zinc,
Water-Soluble Vitamins: Clinical MCQs with Explanations & Illustrations
19
Feb
Test your knowledge of biochemistry and clinical medicine with these high-yield, NBME-style multiple-choice questions on water-soluble vitamins. Each question is case-based to enhance clinical reasoning and exam preparedness.
Biochemistry Challenge- Part 2
24
Nov

"Explore real-world applications of biochemistry through 21 engaging questions that connect metabolic pathways to clinical insights. Tackle scenarios like cyanide poisoning, enzyme regulation, metabolic disorders, and more. Sharpen your critical thinking as you dive into the intricacies of glycolysis, amino acid metabolism, and energy production. A must-read for anyone looking to bridge biochemistry with clinical practice!"
Posted in:
Learning resources ,
Library ,
Practice questions ,
QUIZZES ,
USMLE Content ,
USMLE Style questions ,
USMLE styled question bank ,
Tags:
6-Bisphosphate,
Ammonia Detoxification,
Anaerobic Glycolysis,
Arsenate Poisoning,
Biochemistry,
Collagen mutation,
Cyanide Poisoning,
Cystathionine-β-Synthase Deficiency,
Fatty acid oxidation,
Fructose 2,
GABA Synthesis,
Galactosemia,
Glycogen Metabolism,
lactic acidosis,
Maple syrup Urine disease,
McArdle’s Syndrome,
Metabolic pathways,
Pentose Phosphate Pathway,
PFK-1 Regulation,
Thyroid Hormone,
Tyrosinase Deficiency,
von Gierke’s Diseas,
Clinical Biochemistry Case Studies: Master Carbohydrate, Amino Acid Metabolism & Enzyme Dynamics
24
Nov
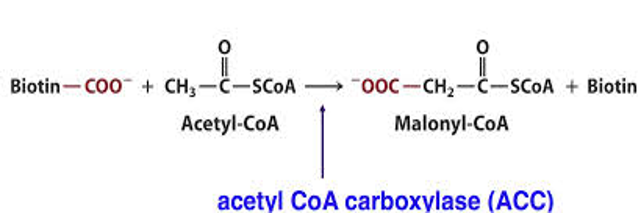
Through 25 hypothetical clinical cases and scenarios, this activity challenges learners to integrate concepts of carbohydrate metabolism, amino acid metabolism, oxidative phosphorylation, and enzyme dynamics. Participants will encounter questions highlighting real-world clinical relevance, such as the role of glycolytic intermediates, gluconeogenesis regulation, enzyme inhibition, and metabolic dysfunction in diseases like vitamin deficiencies and hyperammonemia. This engaging exploration enhances critical thinking and bridges biochemical theory with clinical practice.
Posted in:
Library ,
Metabolism of Carbohydrates ,
Practice questions ,
Quizzes ,
USMLE Style questions ,
USMLE styled question bank ,
Explanations of Quiz on Nucleotide Metabolism
23
Nov
Enzymatic defects in purine and pyrimidine metabolism can present with diverse clinical features, including failure to thrive, megaloblastic anemia, hyperuricemia, or hyperammonemia. Key disorders include UMP synthase deficiency (orotic aciduria), OTC deficiency, ADA deficiency leading to SCID, and Lesch-Nyhan syndrome. Regulation through feedback inhibition and enzyme targets like ribonucleotide reductase are essential concepts for understanding metabolism and clinical interventions.
Posted in:
Metabolis of Nucleotides ,
Metabolism of Nucleotides ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Mutiple-choice questions ,
Practice questions ,
Practice questions ,
QUIZZES ,
Quizzes ,
USMLE Content ,
USMLE Style questions ,
USMLE styled question bank ,
“Clinical Biochemistry: Fatty Acid Metabolism, Ketogenesis, and Energy Regulation”
23
Nov
"Discover key insights into fatty acid metabolism, ketogenesis, and triglyceride synthesis through clinical scenarios. This guide explains enzyme deficiencies like MCAD, hormonal regulation by insulin, and the role of beta-oxidation and omega oxidation pathways in energy production."
Posted in:
Energy metabolism ,
Library ,
Metabolism of lipids ,
Multiple-choice questions ,
Multiple-Choice questions ,
Practice questions ,
Quizzes ,
USMLE Content ,
USMLE Style questions ,
USMLE styled question bank ,
Comprehensive MCQs on Nucleotide Metabolism and Enzyme Deficiencies- A quiz for self-assessment
23
Nov
Dive into a series of multiple-choice questions focused on nucleotide metabolism and related enzyme deficiencies. This collection covers key topics such as UMP synthase deficiency, feedback inhibition mechanisms, purine and pyrimidine synthesis, and metabolic disorders affecting nucleotide pathways. Each question is accompanied by in-depth explanations to enhance your learning experience.
Posted in:
Metabolis of Nucleotides ,
Metabolism of Nucleotides ,
Mutiple-choice questions ,
Practice questions ,
Quizzes ,
USMLE Content ,
USMLE Style questions ,
USMLE styled question bank ,
Tags:
ADA Deficiency,
Biochemistry,
Biochemistry by Namrata Chhabra,
BIOCHEMISTRY FOR MEDICS,
Enzyme deficiencies,
Exam preparation,
Hyperuricemia,
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome,
MCQs,
Medical Education,
Medical students,
Nucleotide metabolism,
Orotic aciduria,
Purine degradation,
purine synthesis,
Urea cycle disorders,
Fatty acid and Triglyceride metabolism- a quiz for self-assessment
22
Nov

"Dear students,
Assess your understanding of fatty acid and triglyceride metabolism with this 32-question timed quiz. Complete it in one sitting and attempt it multiple times to solidify your knowledge. Explanations for all questions will be available tomorrow. Start your self-assessment journey today!"
Posted in:
Energy metabolism ,
Library ,
Lipid Metabolism ,
Metabolism of lipids ,
Multiple-Choice questions ,
Practice questions ,
QUIZZES ,
Quizzes ,
USMLE Content ,
USMLE Style questions ,
USMLE styled question bank ,
